Our research focuses on precision single ion implantation for the realisation of scalable solid state-based quantum technologies. We use and develop state-of-the-art ion implantation tools for the creation of defects and colour centres in different material systems, e.g. NV-centres in diamond.
For scalable quantum technologies, like qubit arrays for quantum computation applications, deterministic single ion implantation techniques are currently under development. “Deterministic” means that not only the spatial precision of single implantation events needs to be optimised, but also at the same time, every single ion arriving at the sample must be detected. Since not only the implantation process itself, but also the sample properties are important to fulfil the various requirements for envisioned applications, we collaborate with the other working groups within the AQS department (Quantum Computer, Solid-state Colour Centres, Applied Quantum Interactions). Within the BMBF Project CoGeQ, the reproducibility, scalability and quantum optical properties of ion implanted NV centres in diamond are investigated with the aim of enabling increasingly large qubit registers. [1]
Leibniz Joint Lab "Single Ion Implantation"
In a close collaboration with the Leibniz Institute of Surface Engineering (IOM) in Leipzig a newly developed single ion implanter is used for fundamental ion implantation studies [2] and to investigate the potential of deterministic ion implantation approaches. This implanter is based on a focused ion beam (FIB) machine, equipped with an electron beam ion source (EBIS), able to produce a nano-focused beam of a variety of ion species and a wide energy range, which is remarkable for such a compact system. [3] The concept of image charge detection is one of the approaches under development to realise deterministic single ion implantation. [4, 5, 6]
DAAD Project-Related Personal Exchange Project
a cooperation with the University of Melbourne and the IOM Leipzig
In the DAAD Exchange project “Optimised diamond-based single ion detection for scalable quantum technologies”, together with the collaboration partners from Prof. David Jamieson’s group at the University of Melbourne and the IOM Leipzig, researchers from the Single Ion Implantation group investigate specialised diamond-based single ion detectors aiming at deterministic single ion implantation for colour centre formation. The project includes several funded research trips of colleagues from Leipzig to Melbourne and vice versa. This research builds upon first results, which originated from a previous DAAD exchange project of the same collaboration partners. [7] An important prerequisite for this project is the possibility to characterise the detectors with a low-energy nano-focused and scanned ion beam induced charge (IBIC) method at the IOM Leipzig, which was developed by scientists from the University of Melbourne and the IOM.
Selected Publications
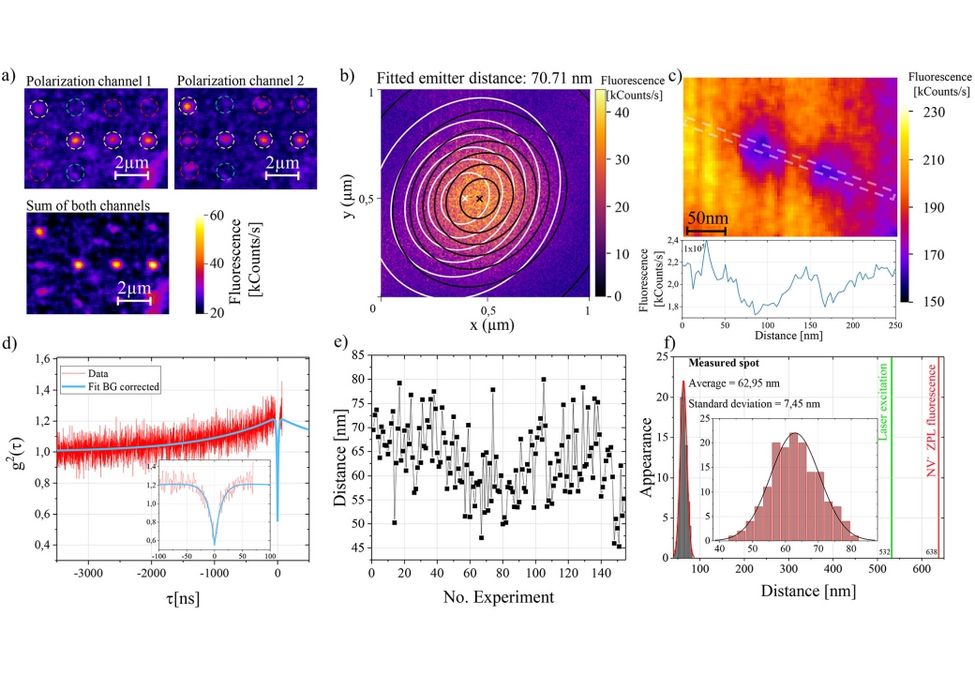
[1] D. Reinhardt, T. Lühmann, P. Räcke, J. Heupel, M. Kieschnick, S. Mändl, C. Popov, J.B. Meijer, R. Wunderlich. Subdiffraction Distance Measurement of Dipolar Emitting Qubit Pairs. ACS Photonics 11, 1382 (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acsphotonics.4c00257.
[2] P. Räcke, L. Pietzonka, J. Meijer, D. Spemann, R. Wunderlich. Vacancy diffusion and nitrogen-vacancy center formation near the diamond surface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 118, 204003 (2021). DOI: 10.1063/5.0046031.
[3] P. Räcke, R. Wunderlich, J.W. Gerlach, J. Meijer, D. Spemann. Nanoscale ion implantation using focussed highly charged ions. New J. Phys. 22, 083028 (2020). DOI: 10.1088/1367-2630/aba0e6.
[4] P. Räcke, J. Meijer, D. Spemann. Image charge detection of ion bunches using a segmented, cryogenic detector. J. Appl. Phys. 131, 204502 (2022). DOI: 10.1063/5.0096094.
[5] P. Räcke, R. Staacke, J.W. Gerlach, J. Meijer, D. Spemann. Image charge detection statistics relevant for deterministic ion implantation. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 52, 305103 (2019). DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/ab1d04.
[6] P. Räcke, D. Spemann, J.W. Gerlach, B. Rauschenbach, J. Meijer. Detection of small bunches of ions using image charges. Sci. Rep. 8, 9781 (2018). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28167-6.
[7] N.F.L. Collins, A.M. Jakob, S.G. Robson, S.Q. Lim, P. Räcke, B.C. Johnson, B. Liu, Y. Lu, D. Spemann, J.C. McCallum, D.N. Jamieson. Graphene-Enhanced Single Ion Detectors for Deterministic Near-Surface Dopant Implantation in Diamond. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2306601 (2023). DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202306601.
BSc/MSc Theses Topics
Systematic investigation of sulphur doping for enhanced NV-centre yield using a single ion implanter (Master thesis)
Contact: Dr. Paul Räcke